Chapter 3: Hardware, Software, and Generative AI
Introduction
Informatics uses technology, information systems, and researching skills to glean new knowledge for decision making. It is important to have knowledge of the makeup of computer systems, software, peripheral devices, both input and output devices, computer components, hard drives, motherboards, CPUs, RAM, what utility software is, how it applies for use and how it is applicable to outcomes. We must also have a basic understanding of how information is stored, inputted, retrieved, and secured.
With the advent and increasing availability and use of artificial intelligence (AI), in particular, generative AI (ChatGPT), we are seeing the use of technology in this realm exploding more than was thought possible, thus greatly impacting the delivery of healthcare.
Learning Objectives for This Chapter
- Introduce in detail communication and collaboration of different information systems and associated personnel.
- Define and apply interoperability through a virtual, hands-on exercise.
- Review and practice with critical information systems via interoperability that are foundational to exploring the concept of interoperability on a theoretical level (i.e., how and why systems do or do not work).
Computers and communication
A personal computer is one that we think about to use at home or even one in an office or other setting that is connected to many other computers, servers, and even systems within an organization, to other organizations using the Internet and even Cloud servers. It is important to know about how systems can integrate and communicate. We do not see how they work in the clinical setting, we just depend on them to work correctly.
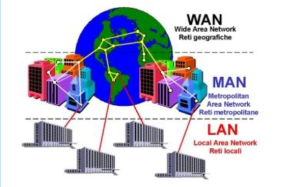
Many of the components you see in the picture are present in the clinical setting and in most organizational settings, even with your own PC or laptop you use. Creating, inputting, and retrieving information and data are ways we use computer systems. In a clinical settings there are systems that are interoperable and interactive–communicating within and between systems. We think of WIFI as how our smart phones work seamlessly from one location to another. In many settings WIFI is the connector for communicating over distance as well as interfacing with systems within a hospital and between healthcare systems. We use the Internet of Things (IoT) everyday with external servers and cloud servers connected through systems via networks. Several are within settings and others connect over distance.
We see Local Area Networks (LAN) in a single building connecting devices users access to do their work. This is also the case in our own home such as having a private network. WIFI provides access for wireless information and with technology where networks use radio waves for high-speed internet access. There are standards that govern how transmissions work and are regulated.
Other types of networks Include MAN or metropolitan area networks with physical connections over or between several existing structures. A communication system in a university with multiple buildings is an example.
The largest and most far reaching is the Wide Area Network (WAN) or what we know as the internet. We also have increasing use of satellites for communication systems including over the internet.
When we think of the internet we see ourselves doing searches on topics, accessing databases for articles, blogs, government organizations, and more. There are several versions such as Web 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and coming is 5.0.
The sophistication of Web 5.0 is in development, and it includes versions 2 and 3. It ultimately is expected to provide users the ability to connect with web sources fully protecting their identity. Two words are used to envision how it will work, telepathic web and symbionet web. It essentially is designed to provide users with control of their own data and protect their identity.
Let’s start with Web 1.0 which provides read only access. This allows us to search and read however, we cannot change any of what we see in the content. We see this when we log into a store and use what is setup as a shopping cart. We can add or delete in the shopping cart but what we click to add, that content cannot change.Web 2.0 is more interactive. We can create, add, and change content with tools such as writing a blog, adding content to a wiki, and even doing presentations with YouTube.
Interprofessionals in healthcare work hand in hand in many different venues across rooms, units, facilities, cities, regions, distances, space and even time. Many disciplines work together across distance synchronously or asynchronously. We can see this in remote connections between critical access hospitals reaching out to diverse specialties in real time such as when there is no internet available in a rural hospital and with the technology connecting to help manage and make clinical decisions.
As was described above it is important to have a foundational understanding of how we use technology, including a basic knowledge of computer components that work with the IoT.
Activity 1
Computer Components
In the image below go to the website by clicking on the image or the link and find all 16 computer parts listed matching each number.
Each of the 16 computer parts (or most) are critical in the operation of the computer terminal in the hospital and personal computers (PCs) including laptops, smart phones, tablets, and other devices for personal use as well as those used in providing healthcare. The smaller and more sophisticated the device we see microprocessors.
File:Personal computer, exploded 6.svg – Wikimedia Commons
Once you have reviewed each item listed, click on each one in the picture then fill in the blanks below to see how many you get correct.
Activity 2
Artificial Intelligence
In the beginning of this book both AI and ChatGPT were mentioned. We would be remiss without inclusion here as much of what we see with the growth, development, and rapid innovative disruption in technology drives more now and going forward. Watch this short video:
What do you think about this video and where technology is leading us?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been around for many years, but more recently moved into the headlines. Machines thinking like humans is the fundamental point of AI, and often it is built on machine learning. Think about how AI computer systems can analyze millions of data to find patterns, themes, connections, and relationships. The computer then uses that data to make decisions, drive healthcare research, as well as diagnosing disease or stages of disease, which would be difficult to do otherwise. Two types of machine learning are basic supervised learning, where algorithms guide for correct predictive output, and unsupervised learning with input of very complex data and the machine analyzes it for relationships, and then makes recommendations based on those relationships. Even more sophisticated is deep learning, performing much more complex tasks with much more data (Pattam, A., 2021). We now are hearing more and more about generative AI.
In healthcare there are differences of opinion about the validity of AI. According to Hudson (2023) the concern by some practitioners is perceptions of the validity of AI leads to misinformation about public health and could misrepresent physicians. Others consider it differently with the strength it brings in research or using generative AI to analyze large amounts of data to help users come up with questions to research or to quickly compare a patients’ pathology to a database of images and be able to make a diagnosis. We can see innovation, disruption ( new ways of what we are doing), and remarkable leaps forward with technology.
We are also hearing and seeing results of ChatGPT (versions increasing) and how it is impacting even everyday life. In late 2022, ChatGPT was introduced by Open AI as an intelligence-enabled chat feature. It is directly connected to generative AI. ChatGPT can converse with anyone and write summaries of topics requested. (Perna, 2023).
According to Cross (2023) there are pros and cons about the viability, safety, reliability, validity , risks and benefits of using ChatGPT. When writing, ChatGPT has volumes of information it can search in seconds and write a paper on a topic of request. A downside is the information it compiles and writes could be plagiarized or not valid information.
Therefore, in education it has pros and cons as well. There are many risks involved in doing so such as cyber crime, copyright, inaccuracies, privacy concerns, and what is generated can be biased, to list a few. If you are using it to collect information and review it closely to correct what might be inaccurate, then it can be quite helpful. Cross (2023) also includes the need to be cautious and there may be legal issues with lawsuits increasing. Yet, there are ways to use this disruptive technology to increase critical thinking skills.
Robots represent another common technology used in many different ways such as in healthcare settings, dangerous environments to prevent injury to people, rehab, social support, incorporating sophisticated AI to power autonomous driving vehicles,

monitoring patients, delivery duties, and much more.
Telepresence using robots is effective in direct communication with patients. It can be used when patients are in isolation to assist in preventing the spread of infection such as experienced with COVID cases. It provides a more human experience connecting remotely to receive stimuli and behave as if actually present in a meeting.
Activity 3
AI and ChatGPT
New innovate and disruptive technologies are emerging, such as AI and Chat GPT. As we see ChatGPT presently has two versions, GPT 3.5 and GPT 4. There are many tasks ChatGPT can do for and with us. They include creating checklists on a topic, writing music, generating new ideas, writing essays, and translating documents into different languages. Generative AI and ChatGPT provides many opportunities to create, develop and grow, including developing critical thinking to improve skills and quality, safe, innovative, and effective decision making.
Conclusion
Technology is developing new and exciting achievements at a rapid pace. Just a few short years ago some of what we see today was considered fiction. Generative AI is providing rapid breakthroughs in every aspect of even our daily lives. AI can search data banks and databases to assist in healthcare research helping to discover new treatments. ChatGPT (version 3.5 [free] and version 4) is impacting all facets, as well. Both however, continue to benefit from human oversight to maintain and increase quality, safety, and improving diversity, ethics, integrity and social justice.
References
Cross, T. (2023, June 10). Is ChatGPT safe to use? What you need to know. SafetyDetectives.
https://www.safetydetectives.com/blog/is-chatgpt-safe-to-use/
Hudson, C. (June, 9, 2023). AI a top issues at this weekends AMA policy meeting. Modern Healthcare.
https://www.modernhealthcare.com/technology/ai-top-issue-annual-ama-meeting
IBM. (n.d.). What is machine learning? Retrieved: October 31, 2023. https://www.ibm.com/topics/machine-learning
Pattam, A. (2021, September 16). Artificial intelligence defined in simple terms. HCLTech. https://www.hcltech.com/blogs/artificial-intelligence-defined-simple-terms
Perna, G. (2023, May 15). Dr. ChatGPT: A guide to generative AI in healthcare. Modern Healthcare.
File: Personal computer, exploded 6.SVG. (2022). Wikipedia commons. File:Personal computer, exploded 6.svg – Wikimedia Commons
Telepresence. (2023). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telepresence
Media Attributions
- laptop is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Video Card is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Networks is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Types of the Web is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Studying Microscope Training
- Group of Interprofessional Healthcare Workers is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Computer Motherboard with attached components is licensed under a Public Domain license
- OpenAI is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- ChatGPT is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Robot 2018 is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Self driving car in San Francisco Bay Area is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Telepresence type robot is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of human beings or animals.
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) is a large language model-based chatbot developed by OpenAI and launched on November 30, 2022, notable for enabling users to refine and steer a conversation towards a desired length, format, style, level of detail, and language used.
"Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer science which focuses on the use of data and algorithms to imitate the way that humans learn, gradually improving its accuracy" (IBM, n.d.)
This can provide experiences with technology necessary for human sensory elements such as vision, sound, and manipulation as well.